Turks
and Caicos
These islands were part of the United Kingdom's Jamaican colony
until 1962, when they assumed the status of a separate crown colony
upon Jamaica's independence. The governor of The Bahamas oversaw
affairs from 1965 to 1973. With Bahamian independence, the islands
received a separate governor in 1973. Although independence was
agreed upon for 1982, the policy was reversed and the islands
are presently a British overseas territory.
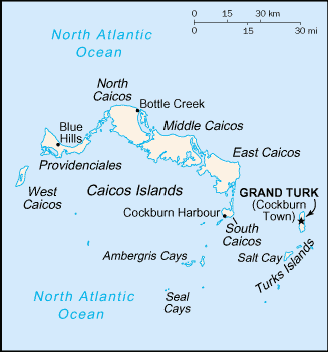
Located in the Caribbean Sea, Turks and Caicos are two island
groups in the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of The Bahamas,
north of Haiti at 21 45 N Latitude, 71 35 W Longitude. Geographically,
the country is about 2.5 times the size of Washington, DC. The
climate is tropical/marine moderated by trade winds, and is sunny
and relatively dry. The islands are made up of low, flat limestone,
with extensive marshes and mangrove swamps. The highest point
is 49 meters above sea level. There are limited natural fresh
water resources, private cisterns are used to collect rainwater
and there are frequent hurricanes. In total, there are about 40
islands (eight inhabited) with a population of slightly more than
19,000.
The Turks and Caicos economy is based on tourism, fishing, and
offshore financial services. Most capital goods and food for domestic
consumption are imported. The US is the leading source of tourists,
accounting for more than half of the 93,000 visitors in 1998.
Major sources of government revenue include fees from offshore
financial activities and customs receipts. Tourism fell by 6%
in 2002 but appeared to be picking up at year end. The official
language is English and the currency is the US Dollar.
Haiti

The native Arawak Amerindians who inhabited the island of Hispaniola
when it was discovered by Columbus in 1492 were virtually annihilated
by Spanish settlers. In the early 17th century, the French established
a presence on Hispaniola, and in 1697, Spain ceded to the French
the western third of the island, now called Haiti. The French
colony, based on forestry and sugar-related industries, became
one of the wealthiest in the Caribbean, but only through the heavy
importation of African slaves and considerable environmental degradation.
In the late 18th century, Haiti's nearly half million slaves
revolted under Toussaint L'Ouverture and after a prolonged struggle,
in 1804 became the first black republic to declare its independence.
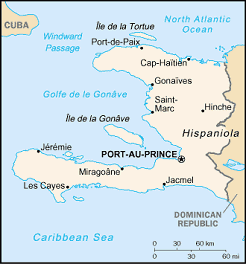
Located in the Caribbean Sea, occupying the western one-third
of the island of Hispaniola, between the North Atlantic Ocean
and the Caribbean Sea, west of the Dominican Republic
at 19 00 N Latitude, 72 25 W Longitude. Slightly smaller than
the State of Maryland, Haiti's climate is tropical and semiarid
where mountains in the east cut off trade winds. The terrain is
mostly rough and mountainous and the highest point is Chaine de
la Selle at 2,680 meters above sea level. Haiti lies in the middle
of the hurricane belt and is subject to natural hazards including
severe storms from June to October; occasional flooding and earthquakes;
and periodic droughts.
Environmental issues include extensive deforestation (much of
the remaining forested land is being cleared for agriculture and
used as fuel), soil erosion and inadequate supplies of potable
water. Haiti shares the island of Hispaniola with the Dominican
Republic (western one-third is Haiti, eastern two-thirds is the
Dominican Republic). Population is about 7.5 million. French and
Creole are the official languages and currency is the "gourde"
(HTG).
Dominican
Republic

Explored and claimed by Columbus on his first voyage in 1492,
the island of Hispaniola became a springboard for Spanish conquest
of the Caribbean and the American mainland. In 1697, Spain recognized
French dominion over the western third of the island, which in
1804 became Haiti. The remainder of the island,
by then known as Santo Domingo, sought to gain its own independence
in 1821, but was conquered and ruled by the Haitians for 22 years.
It finally attained independence as the Dominican Republic in
1844.
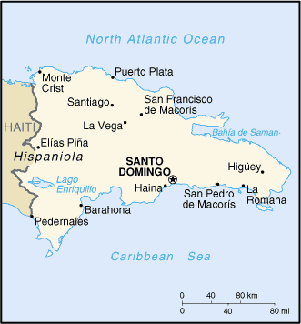
Located in the Caribbean Sea, eastern two-thirds of the island
of Hispaniola, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic
Ocean, east of Haiti at 19 00 N Latitude, 70 40 W Longitude. Slightly
more than twice the size of the state of New Hampshire the climate
is tropical maritime with little seasonal temperature variation
or seasonal variation in rainfall. The Terrain consists of rugged
highlands and mountains with fertile valleys interspersed. The
lowest point is Lago Enriquillo at -46 meters below sea level
and the highest point is Pico Duarte 3,175 meters above sea level.
The Dominican Republic lies in the middle of the hurricane belt
and is subject to severe storms from June to October; Environmental
challenges include occasional flooding, periodic droughts and
water shortages. Soil eroding into the sea damages coral reefs
and deforestation.
The Dominican Republic shares the island of Hispaniola with Haiti
(eastern two-thirds is the Dominican Republic, western one-third
is Haiti). The population is slightly more than 8.7 million. The
official language is Spanish and the currency is the Dominican
peso (DOP).
Jamaica

Jamaica gained full independence within the British Commonwealth
in 1962. Deteriorating economic conditions during the 1970s led
to recurrent violence and a drop-off in tourism. Elections in
1980 saw the democratic socialists voted out of office. Subsequent
governments have been open market oriented.
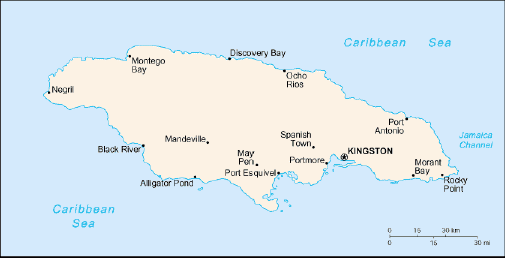
Jamaica is located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba at 18
15 North Latitude, 77 30 West Longitude. The entire island is
slightly smaller than the state of Connecticut, with a total population
of approximately 2.7 million. The climate is tropical, hot and
humid with a temperate interior. The terrain is mostly mountainous
with a narrow discontinuous coastal plain. The highest point is
Blue Mountain Peak at 2,256 meters above sea level. The island
sees frequent hurricanes (especially July to November).
Environmental challenges include heavy rates of deforestation
and the coastal waters are polluted by industrial waste, sewage,
and oil spills causing damage to coral reefs. There is also serious
air pollution in Kingston resulting from vehicle emissions. The
official language is English and the currency is the Jamaican
dollar (JMD).
Puerto
Rico

Populated for centuries by aboriginal peoples, the Spanish Crown
claimed the island in 1493 following Columbus' second voyage to
the Americas. In 1898, after 400 years of colonial rule that saw
the indigenous population nearly exterminated and African slave
labor introduced, Puerto Rico was ceded to the US as a result
of the Spanish-American War. Puerto Ricans were granted US citizenship
in 1917 and popularly elected governors have served since 1948.
In 1952, a constitution was enacted providing for internal self-government.
In plebiscites held in 1967, 1993, and 1998 voters chose to retain
commonwealth status.
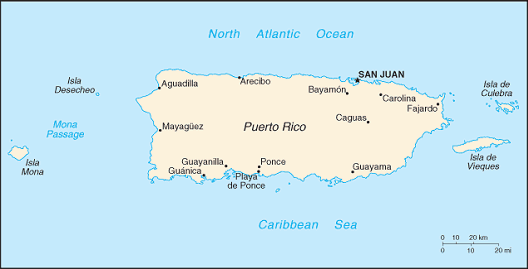
The island of Puerto Rico is located between the Caribbean Sea
and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of the Dominican Republic at
18 15 North Latitude, 66 30 West Longitude. The entire island
is slightly less than three times the size of Rhode Island. The
climate is tropical marine, mild; with little seasonal temperature
variation. The terrain is mostly mountains, with coastal plain
belt in north; mountains precipitous to sea on west coast, and
sandy beaches along most coastal areas. Puerto Rico faces periodic
droughts and hurricanes.
Environmental concerns include erosion and occasional drought
causing water shortages. Puerto Rico maintains an important location
along the Mona Passage (a key shipping lane to the Panama Canal).
San Juan is one of the biggest and best natural harbors in the
Caribbean. The many small rivers and high central mountains ensure
the land is well watered. The population is approximately 3.9
million. Spanish and English are bout spoken in Puerto Rico and
the currency is the US Dollar.
US
Virgin Islands

During the 17th century, the archipelago was divided into two
territorial units, one English and the other Danish. Sugarcane,
produced by slave labor, drove the islands' economy during the
18th and early 19th centuries. In 1917, the US purchased the Danish
portion, which had been in economic decline since the abolition
of slavery in 1848.
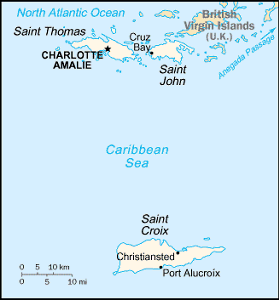
The US Virgin islands are located in the Caribbean islands between
the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Puerto
Rico at 18 20 North Latitude, 64 50 West Longitude. The archipelago
is approximately twice the size of Washington, DC. The climate
is subtropical, tempered by easterly trade winds, with relatively
low humidity and little seasonal temperature variation. The rainy
season runs from May to November. The terrain is mostly hilly
to rugged and mountainous with little level land. The lowest point
is the Caribbean Sea 0 meters and the highest point is the Crown
Mountain at 474 meters above sea level. The Virgin Islands have
experienced several hurricanes in recent years and experiences
frequent and severe droughts and floods. There are also occasional
earthquakes.
Environmentally, the islands suffer from a lack of natural freshwater
resources. The islands hold an important location along the Anegada
Passage - a key-shipping lane for the Panama Canal and Saint Thomas
has one of the best natural deepwater harbors in the Caribbean.
The population is slightly more that 124 thousand. English is
the official language but Spanish and Creole are also spoken.
The US dollar (USD) is the official currency.
British
Virgin Islands
First settled by the Dutch in 1648, the islands were annexed
in 1672 by the English. The economy is closely tied to the larger
and more populous US Virgin Islands to the west; the US dollar
is the legal currency.

The islands are located in the Caribbean, between the Caribbean
Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Puerto Rico at 18 30
North Latitude, 64 30 West Longitude. The archipelago is comprised
of 16 inhabited and more than 20 uninhabited islands including
the island of Anegada. The islands are slightly smaller than Washington,
DC. The climate is subtropical; humid with temperatures moderated
by trade winds. While the coral islands are relatively flat, the
volcanic islands are steep and hilly. The lowest point is the
Caribbean Sea at 0 meters and the highest point is Mount Sage
at 521 meters above sea level. The islands experience hurricanes
and tropical storms from July through October.
There are limited natural fresh water resources except for a
few seasonal streams and springs on Tortola. Most of the islands'
water supply comes from wells and rainwater catchments. The population
is about 21 thousand. English is the official language.
Antigua
and Barbuda

The Siboney were the first to inhabit the islands of Antigua
and Barbuda in 2400 BC, but Arawak and Carib Indians populated
the islands when Columbus landed on his second voyage in 1493.
Early settlements by the Spanish and French were succeeded by
the English who formed a colony in 1667. Slavery, established
to run the sugar plantations on Antigua, was abolished in 1834.
The islands became an independent state within the British Commonwealth
of Nations in 1981.
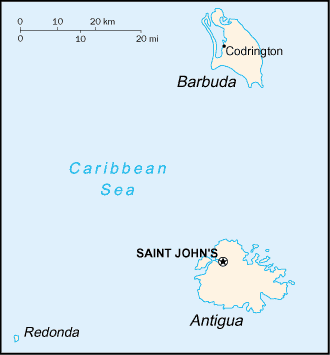
Located in the Caribbean, the islands are between the Caribbean
Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east-southeast of Puerto Rico
at 17 03 North Latitude, 61 48 West Longitude. The islands are
about 2.5 times the size of Washington, DC. The climate is tropical
marine, with little seasonal temperature variation. They are mostly
low-lying limestone and coral islands, with some higher volcanic
areas. The lowest point is the Caribbean Sea at 0 meters and the
highest point is Boggy Peak 402 meters above sea level.
The islands experience hurricanes and tropical storms from July
to October and periodic droughts. Water management is a major
concern because of limited natural fresh water resources and is
further hampered by the clearing of trees to increase crop production,
causing rainfall to run off quickly. Antigua has a deeply indented
shoreline with many natural harbors and beaches while Barbuda
has a very large western harbor. The population is approximately
67 thousand.
English is the official language but there are also some local
dialects spoken. The official currency is the East Caribbean dollar
(XCD).
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe has been a French possession since 1635. The island
of Saint Martin is shared with the Netherlands. Its southern portion
is named Sint Maarten and is part of the Netherlands Antilles
and its northern portion is named Saint-Martin and is part of
Guadeloupe.
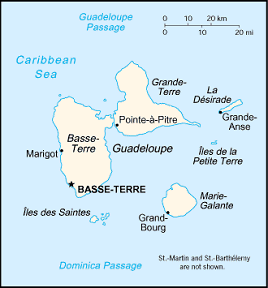
Located in the Caribbean, the islands are between the Caribbean
Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Puerto Rico at
16 15 North Latitude, 61 35 West Longitude. Covering an area of
1,780 square kilometers, making it about 10 times the size of
Washington, DC. Guadeloupe is an archipelago of nine inhabited
islands, including Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La
Desirade, Iles des Saintes, Saint-Barthelemy, Iles de la Petite
Terre, and Saint-Martin (French part of the island of Saint Martin).
The climate is subtropical, but tempered by trade winds with
moderately high humidity. Basse-Terre is volcanic in origin with
interior mountains, while Grande-Terre is low limestone formation.
Most of the seven other islands are volcanic in origin. The lowest
point is the Caribbean Sea at 0 meters and the highest point is
Soufriere at 1,484 meters above sea level.
The islands experience hurricanes from June to October and Soufriere
de Guadeloupe is an active volcano. A narrow channel, the Riviere
Salee, divides Guadeloupe proper into two islands: the larger,
western Basse-Terre and the smaller, eastern Grande-Terre. The
population is slightly more than 440 thousand.
French is the official language, but Creole patois is spoken
by about 1% of the population. There are two official currencies
in the euro (EUR) and the French franc (FRF).
Martinique
Colonized by France in 1635, the island has subsequently remained
a French possession except for three brief periods of foreign
occupation.
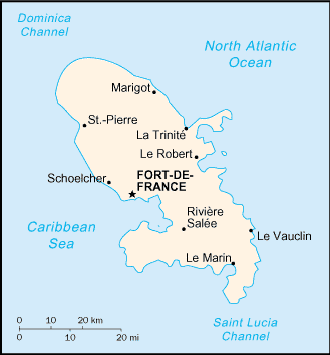
The island is located between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic
Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago at 14 40 North latitude, 61
00 West Longitude. Geographically, the island is slightly more
than six times the size of Washington, DC.
The climate is tropical and humid with temperatures moderated
by trade winds. During the rainy season (June to October) the
island is vulnerable to devastating hurricanes which occur about
every eight years on average. The terrain is mountainous with
indented coastline dominated by a dormant volcano. The lowest
point is the Caribbean Sea 0 meters, while the highest point is
Montagne Pelee at 1,397 meters above sea level.
The island is dominated by Mount Pelee, which on 8 May 1902 erupted
and completely destroyed the city of Saint Pierre, killing 30,000
inhabitants. Population is approximately 426 thousand.
The official language is French, while some Creole patois is
still spoken. The official currency is the euro (EUR).
St.
Lucia

The island, with its fine natural harbor at Castries, was contested
between England and France throughout the 17th and early 18th
centuries (changing possession 14 times); it was finally ceded
to the UK in 1814. Self-government was granted in 1967 and independence
in 1979.
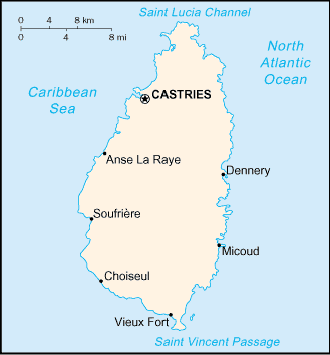
The island is located between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic
Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago at 13 53 North Latitude, 60
68 West Longitude. The climate is tropical, moderated by northeast
trade winds. The dry season runs from January to April and the
rainy season from May to August. The island is volcanic and mountainous
with some broad, fertile valleys. The lowest point is the Caribbean
Sea at 0 meters and the highest point is Mount Gimie at 950 meters
above sea level.
Of geographic note, the twin Pitons (Gros Piton and Petit Piton),
the striking cone-shaped peaks south of Soufriere, are one of
the scenic natural highlights of the Caribbean. The population
is approximately 162 thousand.
The official language is English and East Caribbean dollar (XCD)
is the official currency.
|
![]()